HowTo: Unlock Node Locations
This Loci Memory Palace VR how-to video will demonstrate how to unlock the nodes of a mind map graph and preform a forced layout of the graph. The voice command “unlock nodes” is used. You can also focus the pointer on a node and say “unpin node” to do an individual node.
HowTo: Import Freeplane Mind Maps
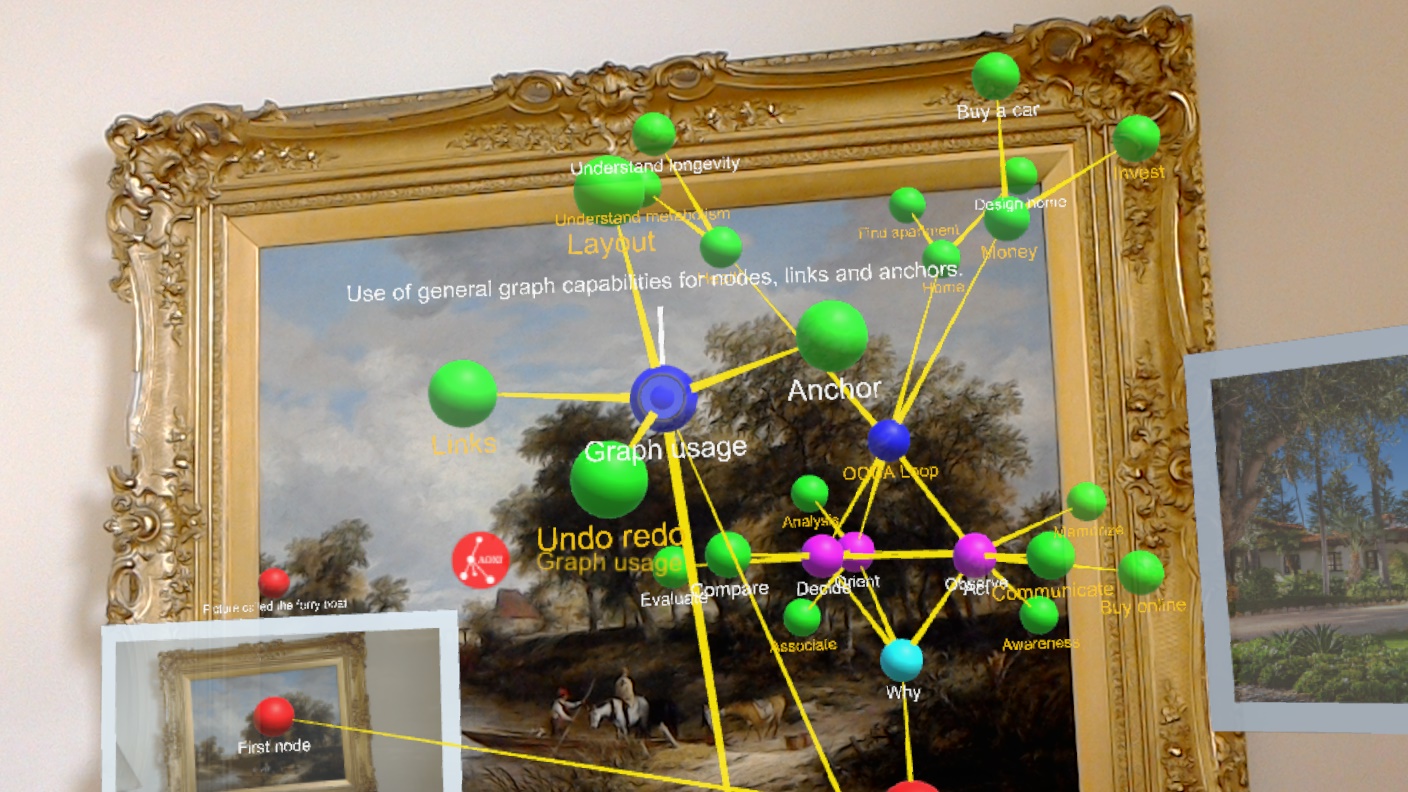
AR 3D Graphs Improve Comprehension over 2D
Most mind maps are shown as 2D views of a graph with central nodes. It is generally better for comprehension to see and interact with a 3D version of the same graph to understand the relations between its nodes.
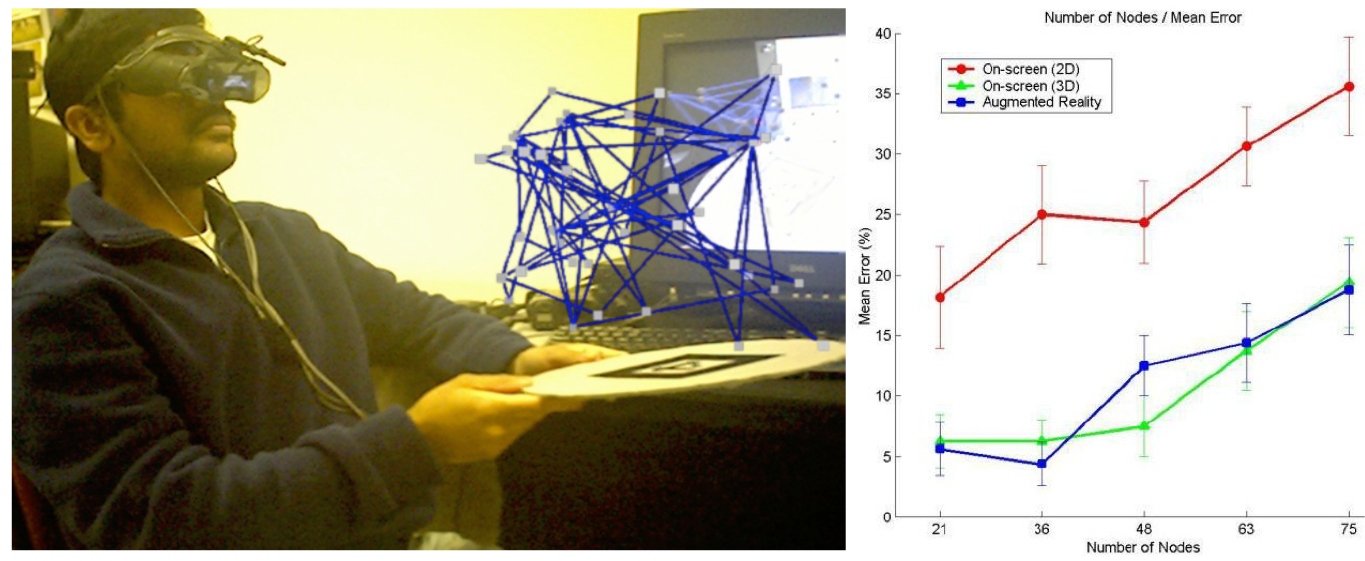
In the paper Using augmented reality for visualizing complex graphs in three dimensions by D. Belcher, M. Billinghurst, S Hayes, and R. Stiles, published in the International Society for Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR) 2003, the study results (link) showed that there is a significant advantage with reduced error for 3D views over 2D views of the same graph when trying to determine if nodes are connected (linked) to each other, which is a key capability when trying to comprehend a graph (or mind map).
The study shows that this improvement of 3D views and interaction with complex graphs also transfers to augmented reality, and not just desktop 3D. In the graph from the paper, you can see significantly reduced node link comprehension error for 3D desktop and AR over the conventional 2D case, and this relationship holds as the number of nodes in the scene scales up.
Loci for AR and VR
Link In YOUR Mind – You Organize, Understand and Recall
Loci currently is provided as two variants; Loci Memory Palace in Virtual Reality on the PC and Loci AR Mind Map in Augmented Reality on the HoloLens. Both have a free seven day trial period and can import mind maps.
Loci uses three core concepts to help you organize, understand and recall; mind maps lets you break a problem down into component parts to organize and do analysis, mixed reality interaction with mind maps lets you visualize in 3D to understand how they are related, and the method of loci persistent placement of mind map nodes lets you improve your recall of the mind map, even when you are not using the Loci software. In this way you can organize your problem, understand it, and remember it later when you need to use that information for decisions.
Loci Memory Palace puts you in a 3D Memory Palace where you can make mind maps using the Windows Mixed Reality headset, and handheld controllers. You can use hand controllers to move, scale or rotate nodes or designate them for voice commands, or to select a place for moving nodes.
Loci AR Mind Map helps you put nodes and links in your own real settings using the HoloLens, such as your home, where you can place your notes and ideas with real items to help you remember and think about them. You can use one or two hand gestures with your own hands to move, scale or rotate nodes.
Both versions of Loci support gaze and voice interaction combined, so that the use of hands or controllers is not required at all times.
Both versions of Loci share the same mind map graph format, *.loci, and both have initial import capability for MindManager, Freemind, and GraphML files. This allows you to bring in your previous mind maps and graphs, as well as mind maps or graph data from other people.
VR Memory Palace Study Shows Recall Improvement
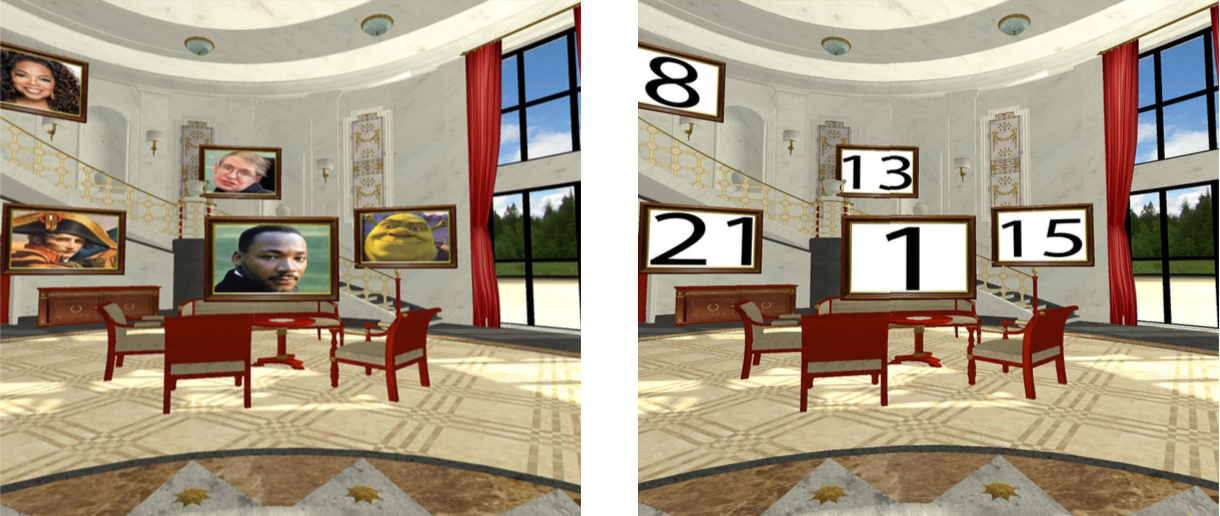
At the University of Maryland College Park, Krokos et al recently published a paper “Virtual memory places: immersion aids recall“, which shows more than 8% recall improvement of a VR memory palace over a desktop memory palace.
The authors provide a nice overview of related work and then describe their study which compared desktop 3D scenes and virtual reality scenes (Head Mount Display – HMD) of a palace and a medieval town as locations to use the method of loci for recall.
The memory task the study participants were to do was recalling two sets of faces and names they saw in these two scenes after two minutes. Strangely, they allowed study participants to rotate their view, but not to translate (move around). Even with this limitation in their study, they found there was a statistically significant effect favoring the HMD (VR) display over the desktop display. Study participants were better able to recall items by 8.8% overall average difference using the HMD over the desktop display.
We have released Loci Memory Palace app for Windows Mixed Reality, which is a virtual reality memory palace populated with nodes and links that are part of your mind map graphs. With Loci Memory Palace, you can move around your memory palace and make mind maps by placing nodes in locations that help you recall. Our Loci app is available now on the Microsoft Store here.
With Loci Memory Palace, you can load images from files and place them in the memory palace, moving yourself and the nodes around in full six degree of freedom. When compared to the conditions of this study, there is more involvement of your body in placing, naming, editing, and associating nodes, and because of this embodiment, involving more of your senses and thoughts, an even greater improvement in recall from using Loci than this study is likely. Your recall of your notes and ideas is available to you even when you are not using our software.
Krokos, Eric & Plaisant, Catherine & Varshney, Amitabh. (2018). Virtual memory palaces: immersion aids recall. Virtual Reality. 10.1007/s10055-018-0346-3.
Abstract: Virtual reality displays, such as head-mounted displays (HMD), afford us a superior spatial awareness by leveraging our vestibular and proprioceptive senses, as compared to traditional desktop displays. Since classical times, people have used memory palaces as a spatial mnemonic to help remember information by organizing it spatially and associating it with salient features in that environment. In this paper, we explore whether using virtual memory palaces in a head-mounted display with head-tracking (HMD condition) would allow a user to better recall information than when using a traditional desktop display with a mouse-based interaction (desktop condition). We found that virtual memory palaces in HMD condition provide a superior memory recall ability compared to the desktop condition. We believe this is a first step in using virtual environments for creating more memorable experiences that enhance productivity through better recall of large amounts of information organized using the idea of virtual memory palaces.
Image of training and test memory palaces for this post is from this paper, used under creative commons license.
Loci Memory Palace
We are proud to announce a mixed reality headset version of our Loci product, called Loci Memory Palace.
Loci lets you link your ideas in augmented or virtual reality, improving recall and links (associations) in your mind. It is an interactive 3D mind map in mixed reality. It runs on Windows Mixed Reality headsets with your Windows 10 PC.
In version 2018.8.1, we have added initial capability to import MindManager, Freemind/FreePlane, and GraphML files. You can say “load graph” or press Ctrl-L on the keyboard and select .mmap, .mm, or .graphml files for import, along with .loci files now. The GraphML importer supports nodes and edges, but does not yet support hyper-edges or ports.
It is available for download on the Windows Store from Microsoft here.
Click this link for info on the Windows 10 mixed reality home.
The headsets are available from HP, Lenovo, Dell, Samsung, Acer and others listed below, for an average of about $300 for a headset. These mixed reality headsets use cameras to sense your surrounding area and position you in a room from the inside out, requiring much less setup than most VR headsets.
- Windows Mixed Reality Overview
- Windows Mixed Reality Hardware Guidelines
- Amazon mixed reality headset example link
- Microsoft Store mixed reality headset page link
We provide a virtual reality location for your ideas and thoughts called the Memory Palace, so you can use the method of loci with immersive virtual reality mind maps.
Updated Voice and Gaze Commands
We updated the set of commands available in the mixed reality memory palace version to reflect capabilities available in that version, the new picture showing commands is below.
Usage in head set with controllers
Use your hand controllers to jump to locations in the Memory Palace, look at a location on the floor and your cursor will follow, then press forward on the controller joy stick to jump to that location.
Use the voice command “add node” to place nodes in the palace rooms. Put in several nodes, one for each thought, then look look at the first node and say “link this”, then look at the next node so the cursor is on it, and say “to that”, and you will see a link appear between them. Gaze at one of the nodes to put the cursor on it, and say “select” to move the node, and the links will update with the node. You are building a mind map graph where the nodes have 3D locations in the memory palace.
Requirements
This version requires Windows 10 Creator’s build, a compatible Mixed Reality Head Mount Display and Controllers, and ideally a graphics card such as NVidia 1060. Most commands use gaze and voice, but moving around in the MR scene is done with the Controllers similar to the way you move and rotate in the Cliff House starting scene. Controllers are usually sold with Mixed Reality headsets.
Improvements
We added mind map and graph imports. Also, with the Creator version of Windows 10, the Load and Save File Picker has better functionality, you can now change the name of the saved file, and both “load graph” and “save graph” come up more reliably with a file picker. Evidently these bugs were fixed in the required separate Onedrive Windows File Picker service.
Known Issues
The first time you run Loci Memory Palace, it will start slowing as the operating system optimizes it for later loads, and you should run it until it shows a dialog box asking to allow voice input, use controller to select “yes” or say “yes”, then you will see the memory palace scene, and then you should exit to the Windows cliff house (HoloShell) by saying “go to start”, then look at the Loci window and say “select” to return back to Loci.
By doing this the Microsoft voice recognition service will work correctly, it seems to provide a reset for it to work after that point. We are still tracking this one down, as it did not happen in earlier versions of Loci. Also, it will be necessary to turn speech services on in your settings, see the fix here.
The HoloShell / Cortona reserved voice command word “select” is not always available while running our app for some reason. It is the default Windows 10 way to select nodes, by gazing so the cursor is on the node and then saying “select” to pick or place a node. Alternatively you can try our voice commands “pick node” and “place node” when moving nodes and select is not available.
Fix MR PC Disk Usage
As you walk around your Mixed Reality, running on your PC with your Immersed Head Mount Display (IHMD) you may tell yourself, “This is not my beautiful house!” because your souped up PC may be running really slow. Mixed reality requires a lot of compute and resource capability.
For general troubleshooting information on getting mixed reality going on your PC, see the Microsoft site here.
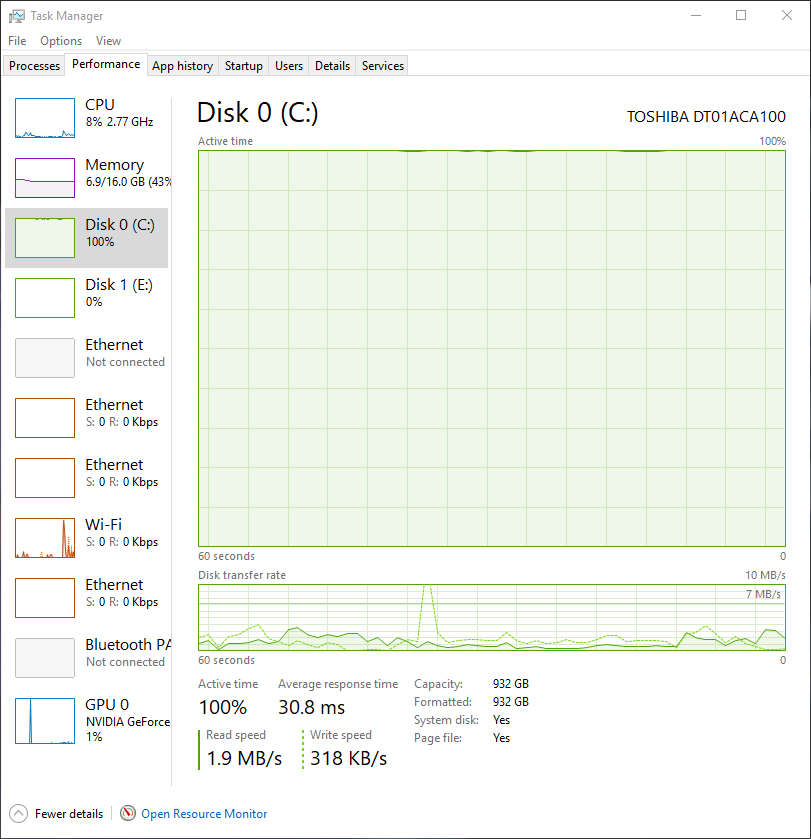
One thing to fix is disk usage. There are at least four culprits that monitor what you do for overall optimization and may get in your way (link and overview):
- Microsoft Compatibility Appraiser
- Microsoft Compatibility Telemetry
- Microsoft SuperFetch
- HP Touchpoint Analytics
To run the msc controls below, press Win+R on your keyboard, and type in the *.msc command for each.
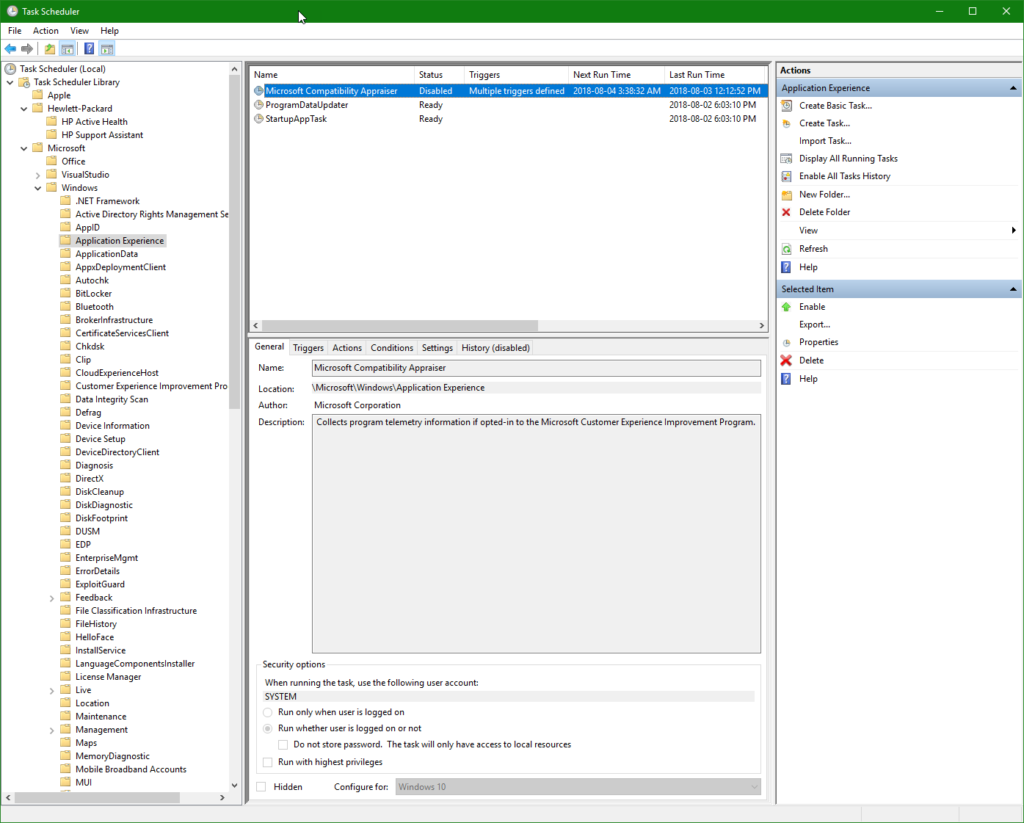
Use taskschd.msc Task Scheduler to disable the MS Compatibility Appraiser ( compattelrunner.exe) as shown in image below.
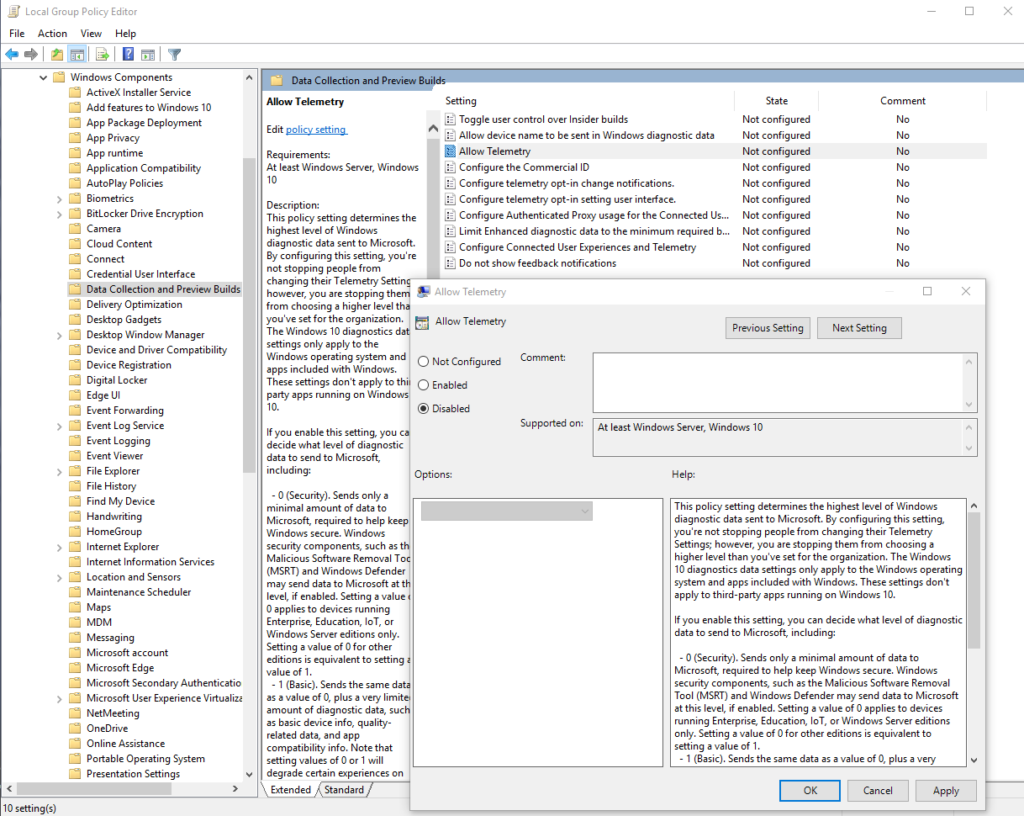
Use gpedit.msc group policy editor to disable the MS Compatibility Telemetry as shown in image below.
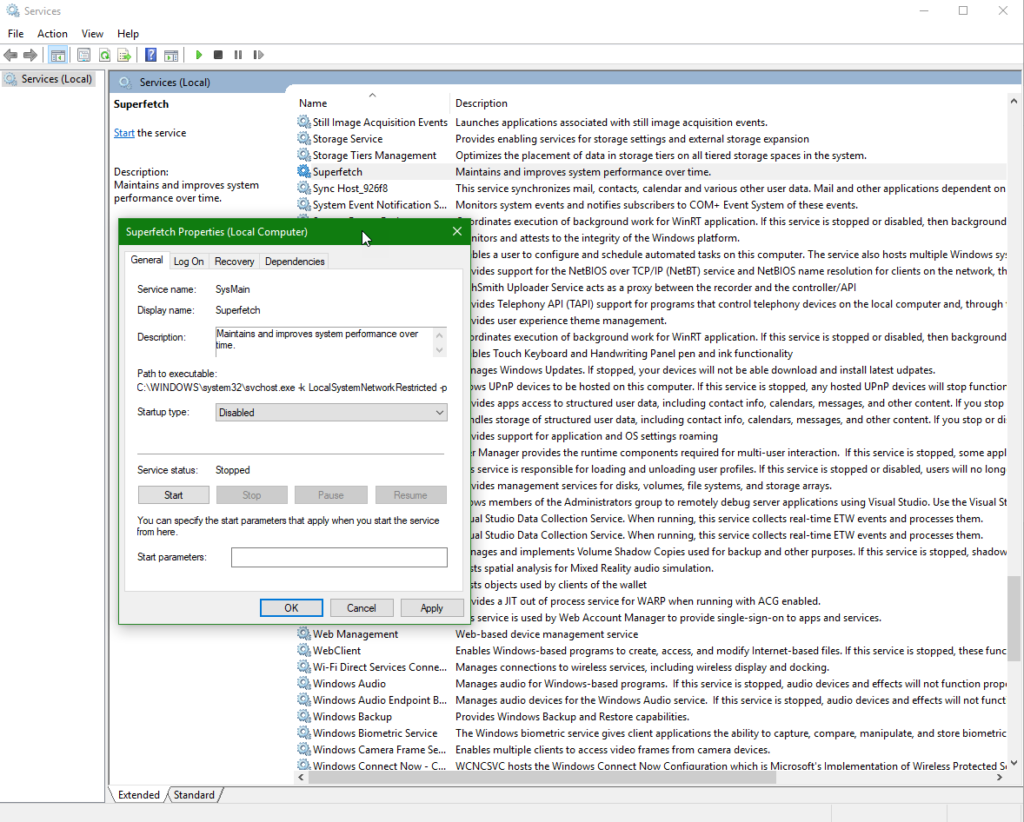
Use services.msc to stop or disable SuperFetch as shown in the image below.
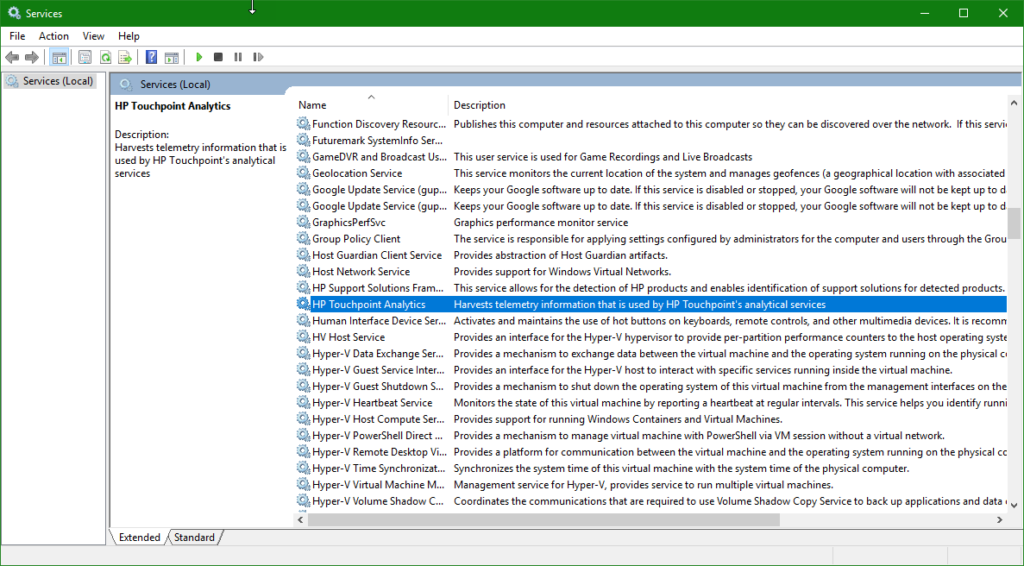
Use services.msc to stop or disable TouchPointAnalytics as shown in the image below. You can then uninstall HP TouchPointAnalytics using Win-R to run appwiz.cpl and search for it to uninstall. For more details click this link.
Loci Voice and Gaze Commands
You use Loci by saying commands and looking at nodes or locations in the scene. Some commands are done only using your voice, and some include where you are looking, your center of gaze.
For Windows Mixed Reality, there are also a large set of useful commands here. These include commands to operating system, like “select”, and commands to Cortona, like “Hey Cortona, take a picture”. In this post we are focused on commands to the Loci application.
It is important to understand that you use your gaze to identify a node that you act on the node with your voice. This is gaze-based selection combined with voice actions (commands).
Generally commands to change the graph are just voice, and commands to change nodes or links include you focusing your gaze onto a node, and seeing the donut cursor on that object.
Our demonstration video, six minutes long, provides examples of using voice and gaze commands: Demo Video
The image of Loci commands in this post is also included as the default image for every node created in Loci. It appears when you start Loci as part of the default scene.
Basic movement of a node is done by looking at it to place the cursor, and saying “Select” which Windows HoloShell uses as a voice command like a left mouse button select, or using an air tap with your index finger. Once you select a node, it locks onto your center of gaze and you can walk and move your head to place it. If you have it where you want it, say select or tap again to place it. It will be locked there for subsequent graph layout, since your chosen locations are very important for using Loci.
When starting out, a very useful voice-only command is “Load Example” which will load an example mind map graph describing the Loci application.
The primary voice commands to use are:
“add node” creates a node at your center of gaze and allows you to use voice to name it and gaze to place it. If you look in mid air, it creates a new unattached node. If you look at an existing node, it adds a new node and conveniently also adds a link to it, and then Loci allows you to name and place the newly added node.
You can add links between nodes by focusing your gaze on a node and saying “Link This” then moving your gaze to another node and saying “To That” and then a link between them will appear. You can delete a link by saying “Unlink This” while gazing at the first node, and then “From That” while gazing at the second node.
“delete node” deletes the node you are looking at (cursor follows gaze onto node). This includes deleting links to that node.
“undo” allows you to undo a prior editing action, such as deleting a node
“select” is a Windows Mixed Reality standard voice command that is equivalent to a finger tap for selecting anything, in Loci it allows you to say “select” when gazing at a node and then place it with your gaze. When you have the node in location, you say “select” again.
Say “name node” when you look at a node and Loci will ask you to provide a short name using your voice for dictation, and change the node name.
On the HoloLens version of Loci, saying “capture image” will use the camera to capture what you are looking at, create a node with your newly captured image shown below it, and allow you to place it.
A very useful set of commands are those for copy and paste.
You center your gaze on a node and say “Copy Node”. This will take all the properties of a node and put them in the copy buffer in a text form. Then you can look at a place in open space and say “Paste Node” and a copy will appear one meter in front of where you were looking. You can also focus your gaze on an existing node, and say the same command “Paste Node” and it will update that node with the properties of the node you have previously copied (Color, scale, name, etc.).
Sometimes you only want to paste certain properties. So you do the command “Copy Node” as usual, and then focus your gaze (cursor) on another node and say paste with a property name, such as “Paste Name” or “Paste Image” or “Paste Color”.
Also see our post on proper Windows 10 settings for voice commands here.
Method of Loci
The method of loci is a memory technique used in ancient Greece and Rome where you imagine a building, and mentally place the items you must remember at locations in the building. Then later you recall these items as you mentally walk through the building and view them in the locations you pass. As this New York Times article on the method of loci describes, the first known published description of this method was in Rhetorica ad Herennium in 80 B.C. Cicero also describes this method in his work De Oratore.
A study of the method of loci published in March 2017 by scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry, the Donders Institute, and Stanford University on the effectiveness of the method of loci showed this technique results in significant recall improvement across time periods of twenty minutes, one day, and four months. Even after four months, the group using the method of loci had more than a 20% level of improvement in recall over the active and passive control groups.
The study included using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) of the subjects, and then comparing their before and after MRIs with memory athletes. They found the method of loci subject’s connections across brain centers came to resemble the memory athlete’s. In their study they show with a figure of the brain’s MRI connections the noticeable difference in connections between memory athletes and controls and indicate this improvement from using the method of loci may result from improved connections (links) across brain areas.
Our Loci app is available now for Windows Mixed Reality on the Microsoft Store here. Using Loci, you link in your mind. You place nodes with camera or file images, web links, or text at locations in your home and office. You can link them to form mind map graphs or you can leave them unattached as a form of pinned note. In either case you have placed them in a location, reinforcing your memory of them for recall at any time, even when not using the Loci application. Furthermore, you can share your mind map graphs with others, taking the method of loci from one person’s internal thoughts to an external visualization that can be communicated digitally with other contributors.